The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. It contains over 500 medicines and can be downloaded as a (74 page) PDF from the WHO website. There is also an electronic version.
This list will not contain over 500 medicines…
But it will have some of them, along with any interesting factoids. If you want to use a drug and the dose isn’t here (or isn’t immediately obvious) you should probably get into the room somebody that is more familiar with the drug. Referencing in this note is intentionally sparse as it would be lengthy and no more helpful than a selection of good textbooks.
Most drugs will have a skeletal formula as well as an accompanying table. In the table:
- On is the onset of action (not necessarily the time to appreciable serum concentrations)
- Off is the author’s small brained synthesis of things such as the duration of action and the half-life
[w] next to the heading is a warning: the drug may have serious of irreversible adverse effects, or requires some other flavour of caution.
[b] next to the heading indicates a specific brand.
Actrapid [b]
Recombinant human (neutral) insulin produced by Novo Nordisk in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Human neutral insulins are homologous with endogenous insulin, but rapid-acting insulins such as Novorapid are favoured due to their more desirable pharmacokinetic profiles.
Dosing
- Depending on requirements.
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30-60mins (SC) | 8 hours | Site of action (by endocytosis) protein-disulfide reductase (glutathione) | Urine |
Neutral insulins can be given intravenously; by this route, the onset of action is immediate.
Adrenaline
Or as the Americans call it, epinephrine. It is an endogenous catecholamine that essentially induces a sympathetic response (and thus creatively referred to as a sympathomimetic). It does this mostly because when one squirts 1000 micrograms of the stuff into the bloodstream nature’s carefully turned receptor affinities go out the window. Noradrenaline is more instrumental in regulating the sympathetic nervous system, but that is discussion to be had elsewhere
Dosing
- 500mcg IM for anaphylaxis.
- 1mg IV for cardiac arrest.
- Children: 10mcg/kg for both.
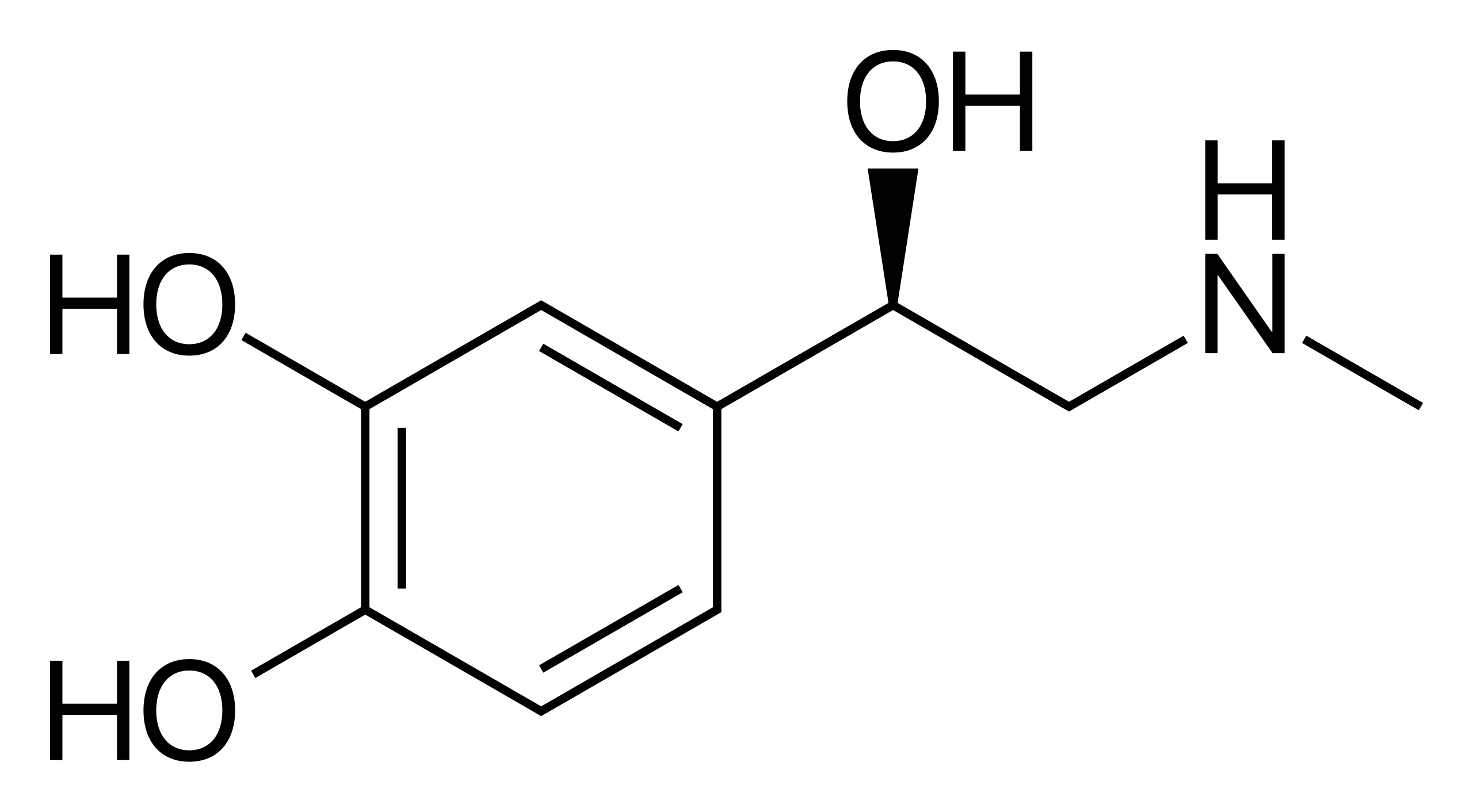 By Roland Mattern - Public Domain, link
By Roland Mattern - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolisation | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seconds | A few minutes | Adrenergic synapse: Monoamine oxidase COMT | Urine |
Allopurinol
Used for the treatment of gout as a urate lowering agent. It, but mostly its primary metabolite oxypurinol, inhibit xanthine oxidase and prevent the multi step oxidation of hypoxanthine to uric acid.
There is some talk about the resultant increase in hypoxanthine leading to (negative feedback) inhibition of de novo purine synthesis. Hypoxathine can be salvaged for synthesis of guanosine and adenosine nucleotides.
Dosing
- 100mg PO daily for gout, increased until target serum urate is achieved (<0.3mmol/L). Not to be commenced during an acute gout attack.
- 300mg PO daily for prophylaxis of TLS, commencing at least 2 days before chemotherapy. Ensure adequate hydration.
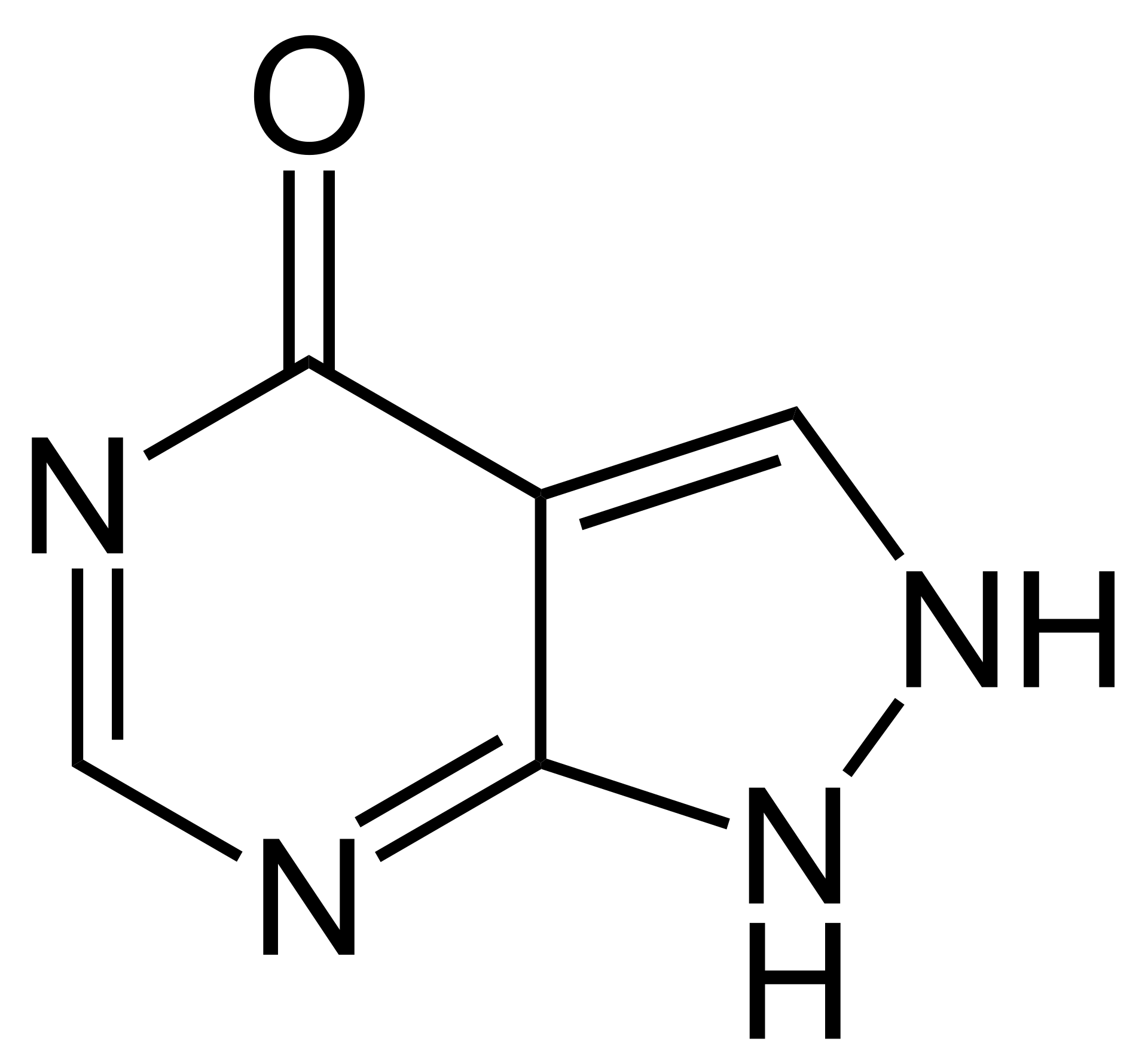 By Jü - Public Domain, link
By Jü - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Days | About a day | Liver Aldehyde oxidase | Urine |
Perhaps the most interesting thing about allopurinol is the enzyme that metabolises it; aldehyde oxidase requires molybdenum as a cofactor. It is a member of the flavoprotein family, using flavin adenine dinucleotide as another cofactor.
Amiodarone
Amiodarone is for some reason advertised as a class III antiarrythmic medication, but it is actually also a class I, II, and IV… It’s use in cardiac arrest is not really supported by any evidence.1 It comes as a besilate salt.
Dosing
- 300mg IV for ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, after the 3rd shock.
- Usually 200mg daily for the maintenance of antiarrythmic therapy.
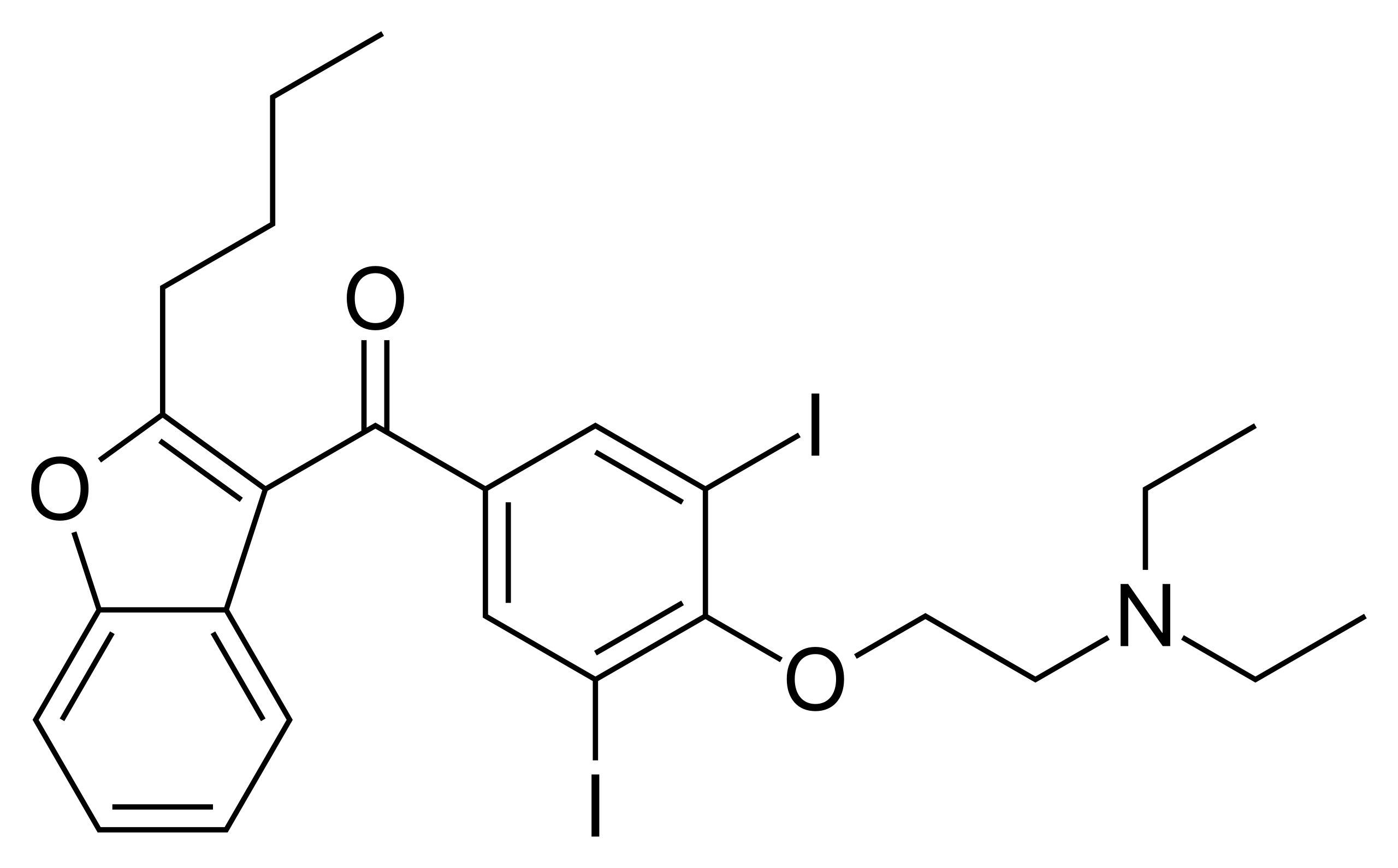 By Vaccinationist - Public Domain, link
By Vaccinationist - Public Domain, link
Note the two iodine atoms, which are responsible for its poor collegiality with the thyroid gland. It produces the Wolff-Chaikoff effect, which may cause hypothyroidism in some patients.
It is also a vesicant, and in New Zealand the solution for injection comes in an ampule from Slovakia with a pH of about 4.0, it is declared incompatible with saline and all kinds of other things (DHEP and the plasticisers in PVC infusion sets).2 If you infuse it, historical wisdom would have you do so with 5% dextrose.
While rare, its penchant to turn peoples’ skin a blue-grey colour is fascinating. Unfortunately the mechanism of this escapes the author, but surely it is related to deposition of something or other in the skin. One might read somewhere about the Tyndall effect…
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow (?) | (???) | Liver CYP3A4 | Liver, bile |
The absorption of amiodarone is slow and unpredictable. It is lipophilic, has a big beautiful volume of distribution, and its primary metabolite is also pharmacologically active. No surprise then that the half-life easily might exceed 59 days.
Amlodipine
A extensively prescribed dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, used principally for the treatment of hypertension (and sometimes for angina).
Dosing
- 5mg PO daily (max 10mg daily).
By Jü - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hours (peak effect at 6-8 hours, oral) | About a day | Liver CYP3A4 | Urine |
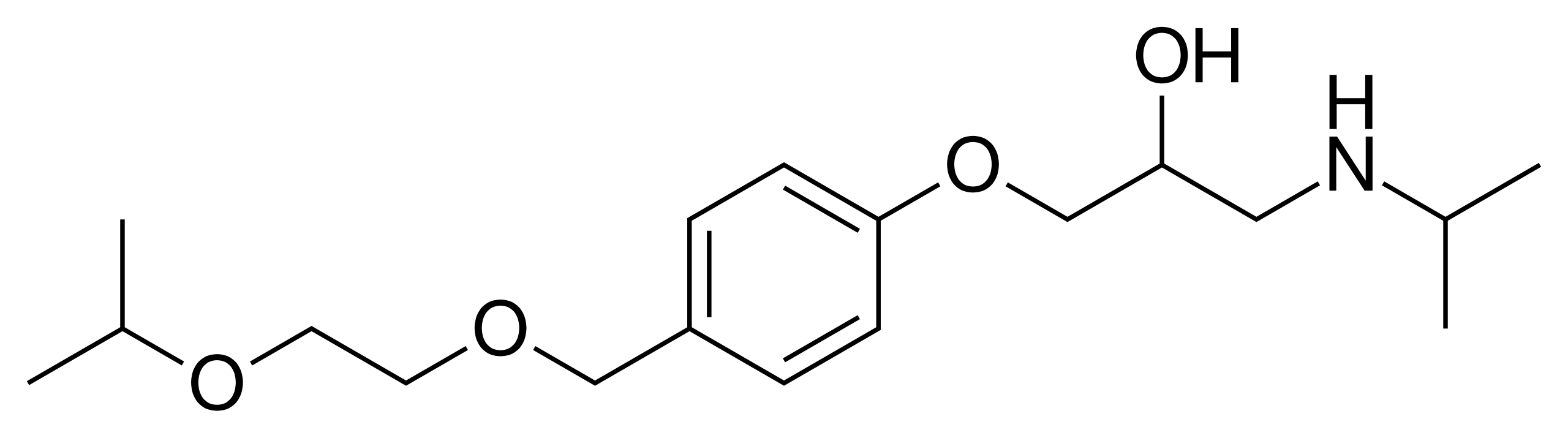
Bisoprolol
Bisoprolol is a β-blocker that is highly β1-selective. It is used for the management of hypertension and as one of the four pillars of heart failure management. It comes as a salt of fumarate and has on oral bioavailability of about 90%.
Dosing
- 10mg PO daily for hypertension, max 20mg.
- For (stable chronic) heart failure, starting at 1.25mg PO daily and increasing to 2.5mg if tolerated, Then increasing by 1.25mg monthly according to response.
 By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| A couple of hours | About half a day | Liver CYP2D6 CYP3A4 | Urine (50% unchanged) |
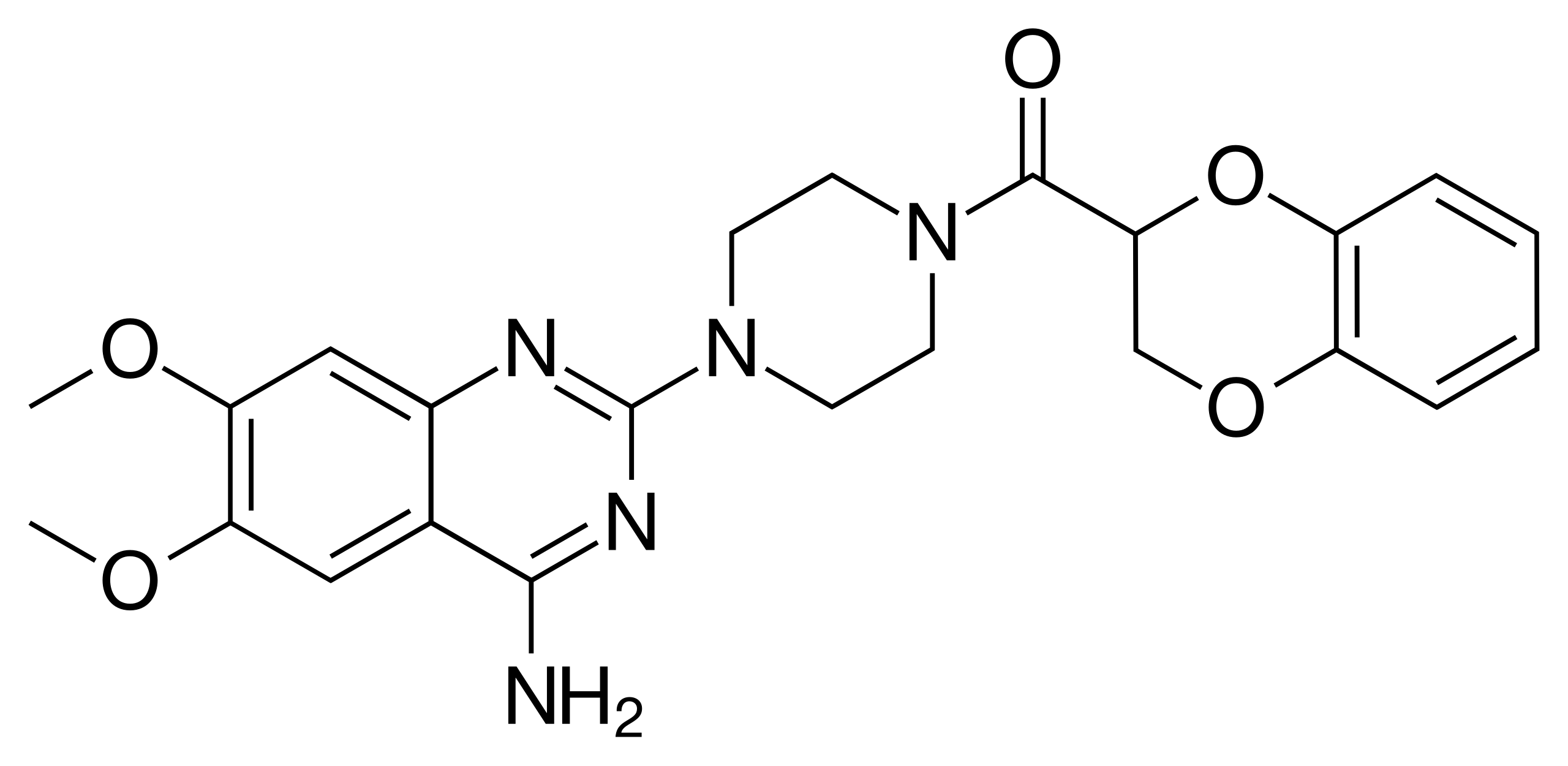
Doxazosin
Doxazosin is a competitive selective α1-blocker, its parent compound is quinazoline. It decreases total peripheral resistance by blocking the effects noradrenaline at the α1 receptor in vascular smooth muscle; the theory is that the same relaxation occurs in the anterior fibromuscular stroma of the prostate, treating BPH.
Dosing
- Initially 1mg PO daily for hypertension and BPH, usual maintenance 2-4mg.
- Max 16mg for hypertension, max 8mg for BPH.
 By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 hours | 1 day | Liver CYP3A4 | Faeces |
Doxazosin is typically presented as a mesilate salt, despite not usually being advertised as such.
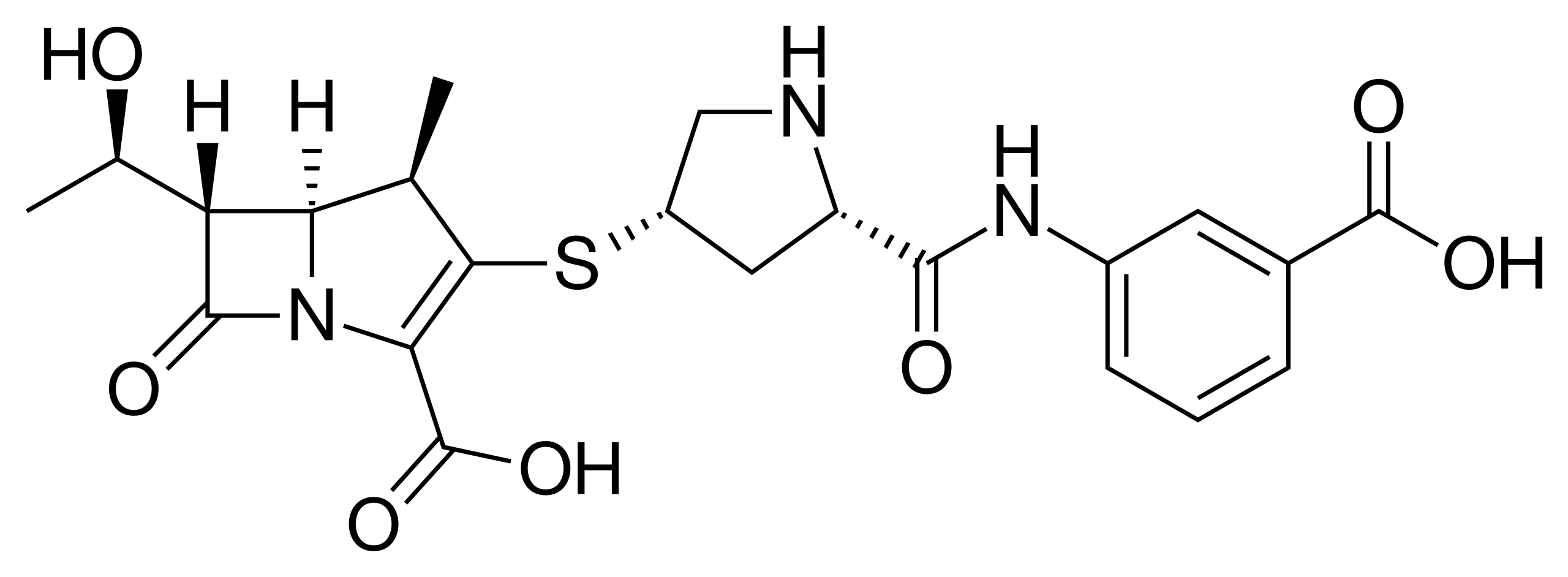
Ertapenem
Ertapenem is a carbapenem antibiotic and probably a drug of last resort in New Zealand, infectious disease would like to be involved in its prescription. It comes as a sodium salt, in a lyophilised powder for injection. Meropenem is used (slightly) more routinely.
For intramuscular administration, the New Zealand formulary advises reconstitution with 3.2mL of 1% lidocaine followed by immediate injection.
Dosing
- 1g IV daily for severe infections (with a few Hail Marys).
 By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 hours | Several hours | Liver CYP 450, multiple isoforms | Urine |
The carbapenems are a type of β-lactam antibiotic and exert their bactericidal effect by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis. The β-lactam ring acetylates the Ser62 residue of bacterial penicillin binding proteins, a subtype of D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase. This irreversible binding inhibits the enzyme’s ability to form the cell wall peptidoglycans.
There is a potential risk of allergic reaction in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to other β-lactam antibiotics, caution is advised.
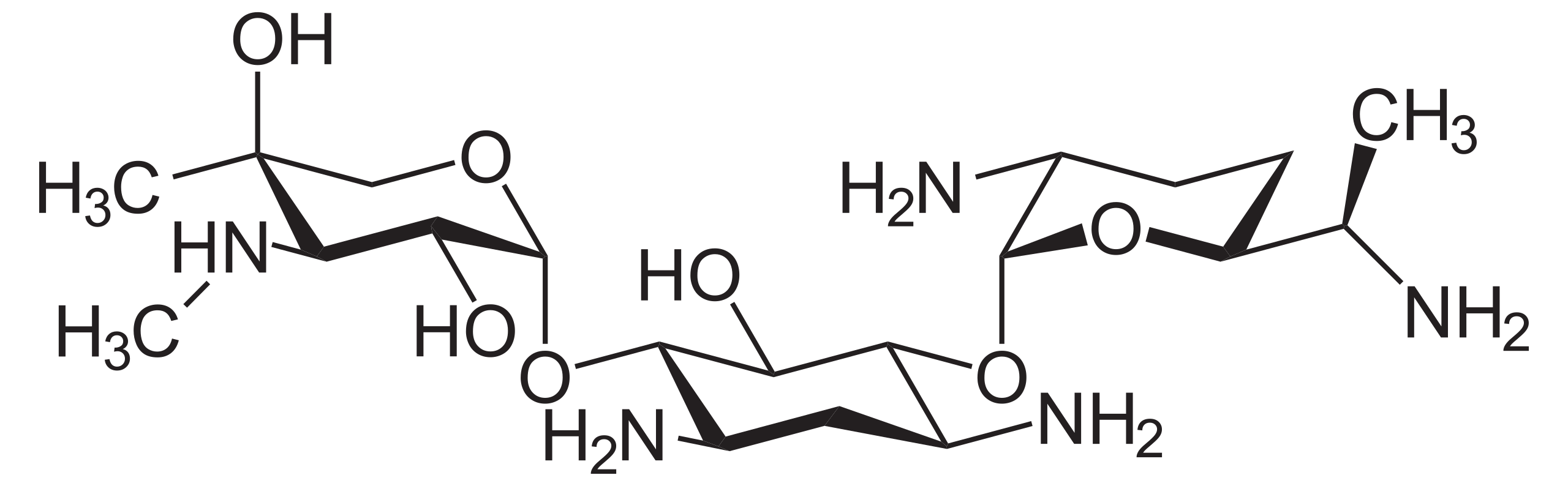
Gentamicin [w]
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used in the treatment of infection by aerobic gram negative organisms (and staphylococcus spp.). It binds irreversibly to the 16S ribosomal RNA of the 30S (prokaryotic) ribosomal subunit, interfering with protein synthesis and leading to death of the organism. It is comes as a sulfate salt; it is not orally bioavailable.
Dosing
- Usually 5mg/kg(ideal body weight) IV daily, with serum levels at 30mins and 12hours after infusion.
- For patients with an eGFR ≤40: 3mg/kg(ideal body weight)
- 7mg/kg(ideal body weight) IV daily for severe sepsis, with serum levels at 30mins and 12hours after infusion.
- Ask infectious disease for help in patients with an eGFR ≥20.
- Involve the ward pharmacist for dose adjustment after commencing therapy.
These dosing rules also apply to tobramicin.
 Gentamicin C2.
By NEUROtiker - Public Domain, link
Gentamicin C2.
By NEUROtiker - Public Domain, link
Gentamicin is actually a group of related compounds, there are three groups (A, B, and C); group C has the highest antibacterial activity. It is produced by some members of the genus micromonospora, particularly M. purpurea which the author can find little information about. It is said that this drug got its name because when cultured the bacterium by which gentamicin is produced exhibits a purple colour due to gentian violet.3
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| An hour or two | Several hours | Not metabolised | Urine |
Continuation of gentamicin therapy should be guided by antibiotic sensitivities, as well as any exhibited nephrotoxicity or ototoxicity. The nephrotoxicity is usually reversible on withdrawal of the drug, however ototoxicity is more likely to be permanent.
Neuromuscular blockade has been reported in cats receiving doses in excess of four times the standard human dosing.4 The manufacturers advise caution in patients with neuromuscular disorders or those undergoing anaesthesia with curare-like paralytic agents.
Naloxone
It appears the only trade name in regular use is Narcan. Naloxone is a competitive multi opioid receptor antagonist (μ > ẟ > κ) used for the reversal of narcosis (usually to fix respiratory depression); its mechanism of action is poorly understood. It comes as a hydrochloride salt.
Dosing
- Depending on severity, up to 400mg IV initially (consider 100-200mg to prevent pain crises).
- 800mg if no response to initial dose after 1 minute, then 800mg, then maybe 2g.
 By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
By Fvasconcellos - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 mins | 1 hour | Liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferases | Urine |
Naloxone is also available as a nasal spray at a dose of 1.8g and may be stocked by a nearby establishment incase you ever need it.
There is no evidence that it causes dependence, nor other untoward effects if administered in the absence of narcotics (though it may impede the response to endogenous opioids).
Novorapid [b]
Also manufactured by Novo Nordisk, Novorapid is insulin aspart. It is another recombinant insulin produced in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Insulin aspart has a single aspartic acid substitution (p.Pro28Asp). Together with insulin glulisine (Apidra by Sanofi), and insulin lispro (Humalog by Eli Lilly), it is a rapid acting insulin with a shorter duration of action.
Dosing
- According to requirements.
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15mins | 3-5hours | Presumably the same as other insulins | Urine |
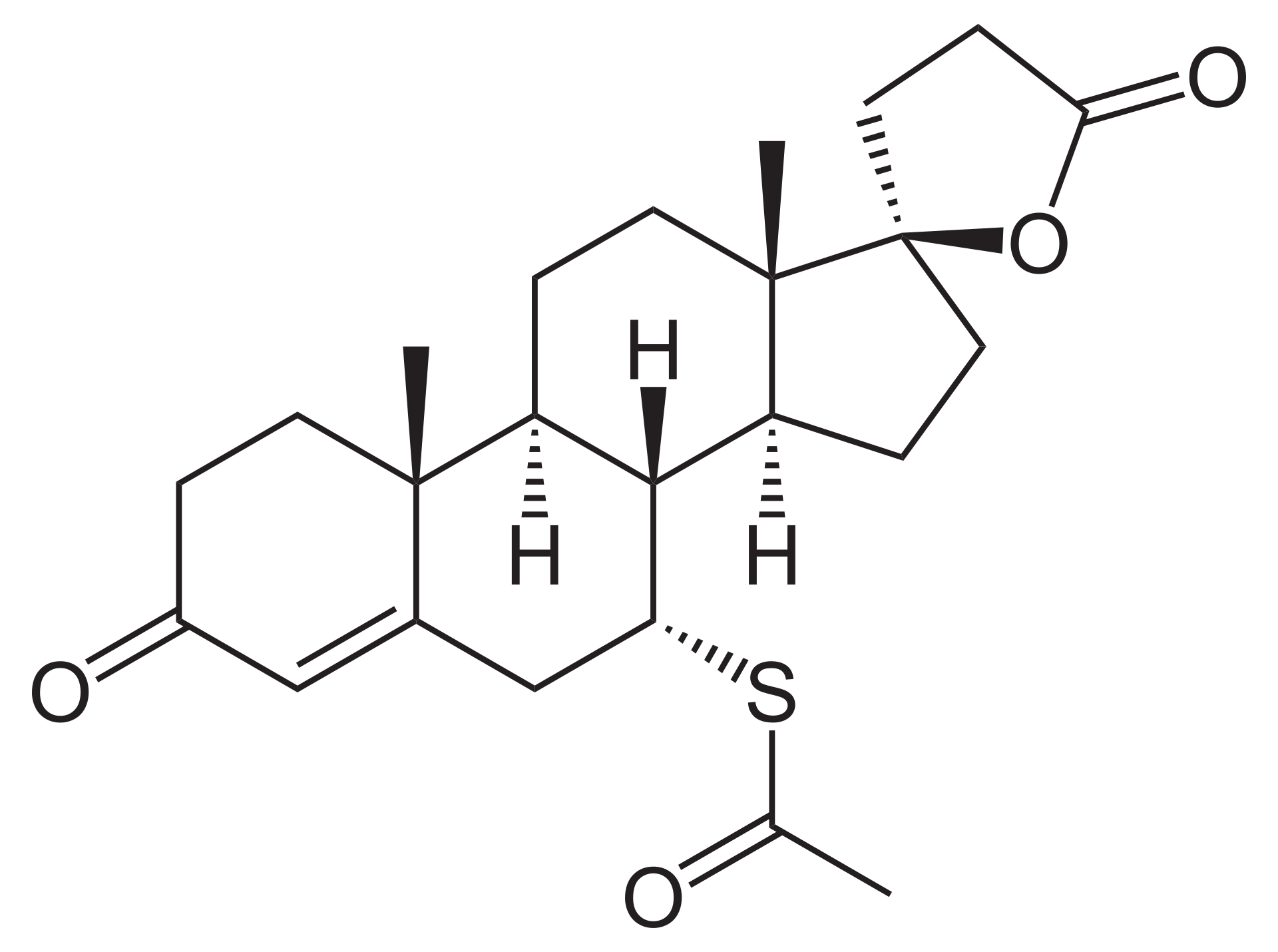
Spironolactone
Spironolactone is a non-selective mineralocorticoid antagonist: or an aldosterone antagonist. It is one of the few potassium sparing diuretics and acts primarily at the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct promoting excretion of sodium and water. The antialdosterone effect downregulates both the basolateral sodium potassium exchanging adenosinetriphosphatase and the epithelial sodium channel; the net effect is reduced interstitial influx of sodium and consequently decreases reabsorption of water from the urine.
Dosing
- 25mg PO daily for heart failure (rEF), max 50mg daily.
- 25mg PO daily for resistant hypertension (fourth line).
 By NEUROtiker - Public Domain, link
By NEUROtiker - Public Domain, link
Regardless of whether or not spironolactone is biologically active, its half life is under two hours which makes it a rubbish drug for one daily pill taking. How convenient then, that it is a prodrug for active metabolites with much more respectable half-lives (in excess of 12 hours). The 7ɑ-[whatever] metabolites, of which there are many, produce the therapeutic effects. The most important are 7α-thiomethylspironolactone and canrenone.
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 or 3 hours | About a day | Liver take you pick | Urine |
Your homework, dear reader, is to think up the skeletal diagram for 7α-thiomethylspironolactone, it it not much different of that of spironolactone above…
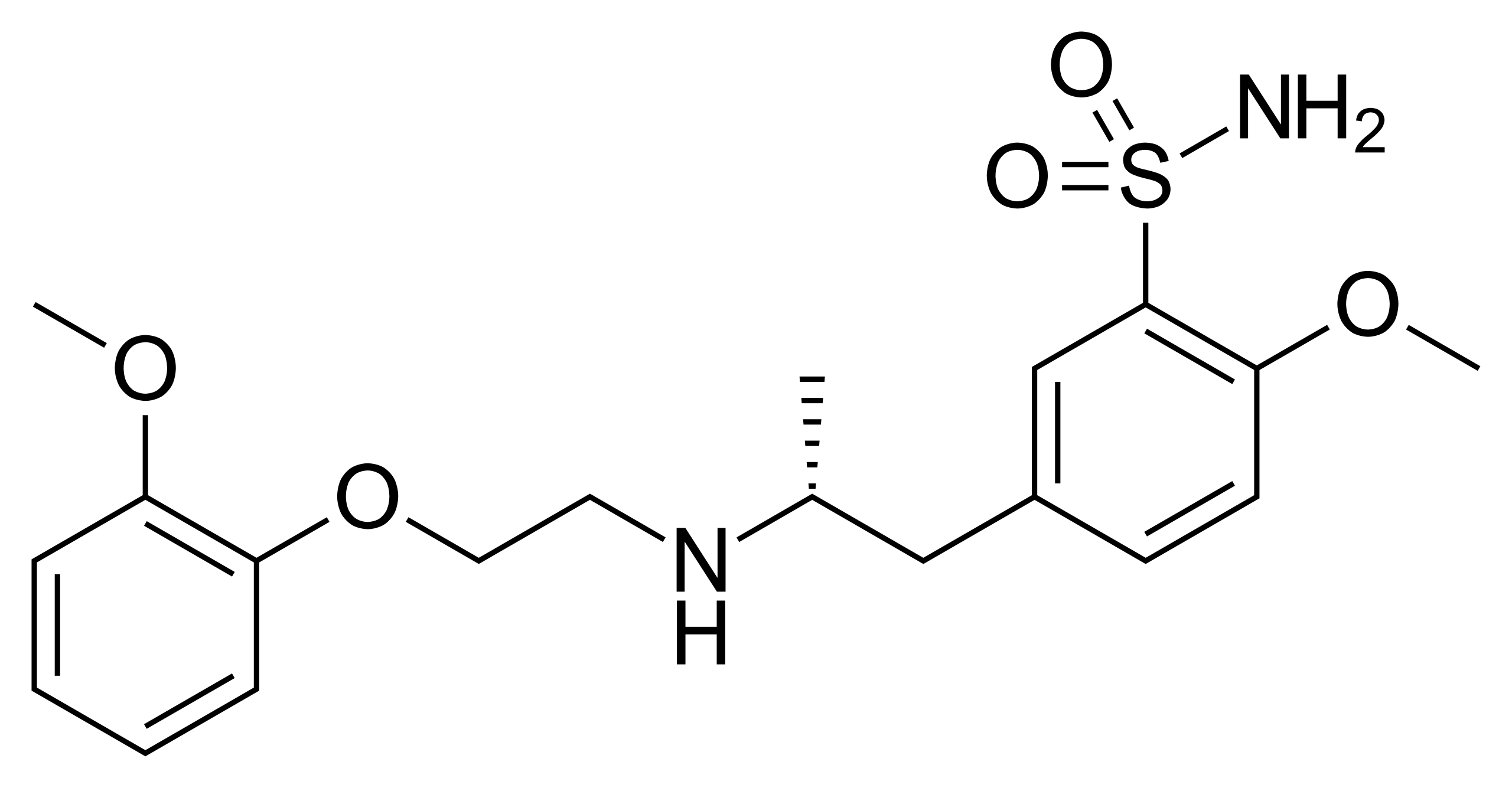
Tamsulosin
This α-blocker has preference for the A (and D) subtype of the α1-receptor. It decreases the obstructive symptoms of BPH by causing smooth muscle relaxation in the anterior fibromuscular stroma of the prostate.
Dosing
- 400mcg PO daily for the treatment of BPH.
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hours | >12 hours | Liver CYP3A4 also CYP2D6 | Urine |
In its pharmaceutical form, only the R(-) enantiomer is present; it comes as a hydrochloride salt. There is not in vivo conversion to the S(-) enantiomer which has less biological activity.
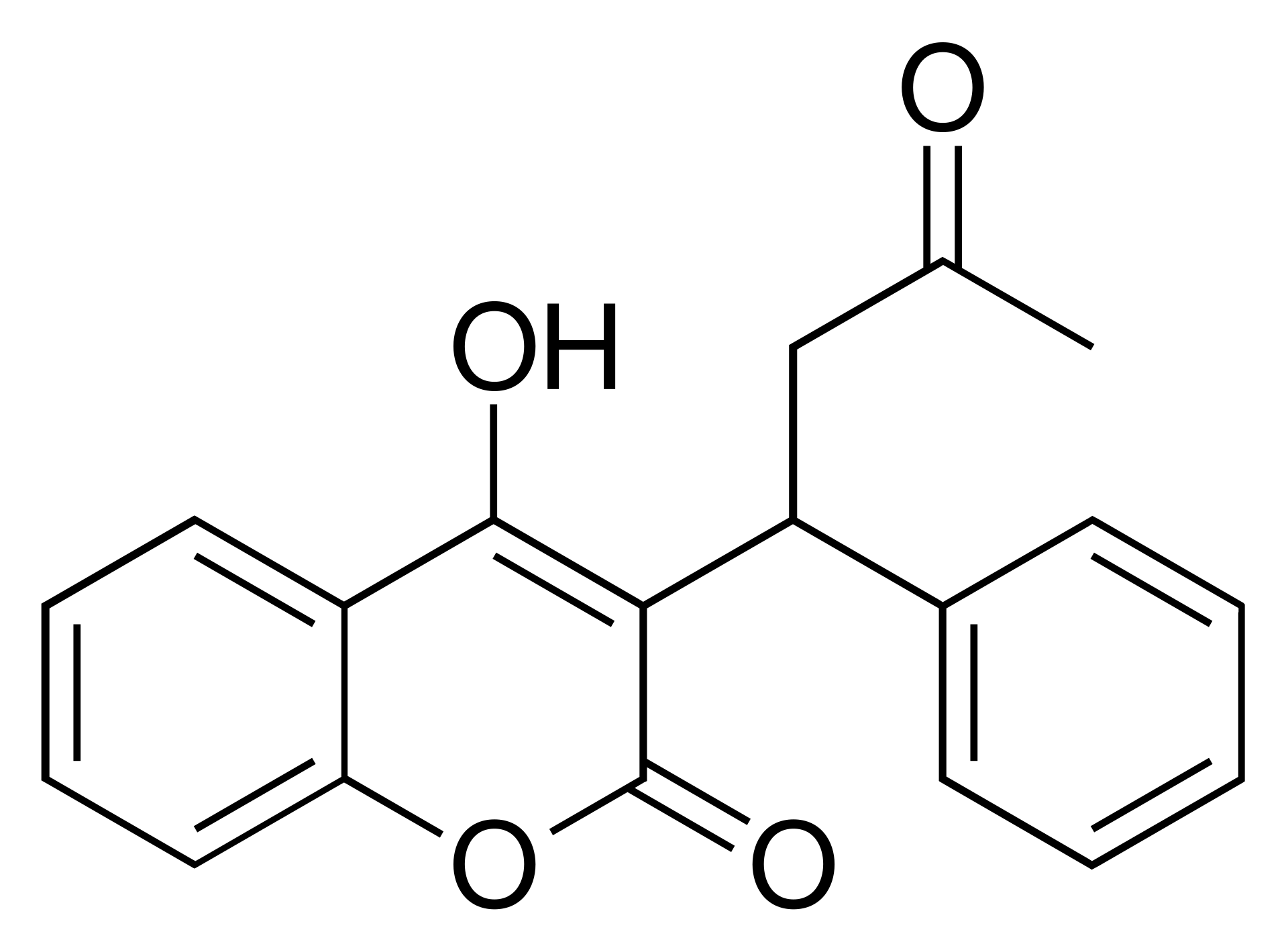
Warfarin
The only 4-hydroxycoumarin in routine medical use (there are plenty others used as rodenticides), warfarin is an antagonist of vitamin K epoxide-reductase and ultimately prevents γ-carboxylation of the vitamin K dependent coagulation factors.
Dosing
- Load at 5-10mg PO on days 1 and 2 with INR monitoring.
- Usual maintenance 1-10mg according to INR.
 By Calvero - Public Domain, link
By Calvero - Public Domain, link
| On | Off | Metabolism | Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Days | Also days | Liver CYP1A2 CYP3A4 CYP2C9 | Urine |
The name warfarin is derived from Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation who presumably funded the research at Wisconsin University about a decade after Frank Schofield, better know for being a Korean independence activist, discovered that a bovine haemorrhagic sickness was a result of the cows eating mouldy sweet clover.5 The suffixed -arin refers to coumarin, the compound metabolised to dicoumarol by whatever microorganism spoiled the sweet clover back in the 1920s.
Further reading
Footnotes
-
Yartsev A. Amiodarone | Deranged Physiology [Internet]. [cited 2025 Nov 11]. Available from: https://derangedphysiology.com/main/cicm-primary-exam/cardiovascular-system/Chapter-967/amiodarone ↩
-
Sponsor: Max Health Limited. Cordarone X Data Sheet [Internet]. Medsafe; [cited 2025 Nov 11]. Available from: https://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/datasheet/a/amiodaroneinj.pdf ↩
-
citation needed ↩
-
Sponsor: Pfizer New Zealand Limited. DBL(TM) Gentamicin Injection BP Datasheet [Internet]. Medsafe; 2022 [cited 2025 Nov 20]. Available from: https://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/datasheet/d/DBLGentamicinBPinj.pdf ↩
-
Schofield FW. A Brief Account of a Disease in Cattle Simulating Hemorrhagic Septicaemia due to Feeding Sweet Clover. Can Vet J. 1984 Dec;25(12):453–5. ↩